What is GRC?
Being an institution with risk intelligence is an inevitable approach in the current period. Almost all of our business processes are at risk, and losses can be more devastating than ever before. For this very reason, regulators and stakeholders want companies and institutions to have more control and manage risks that may affect all business processes and operations.
From market volatility and regulatory compliance to human nature and technology, there is the potential for uncertainty in everything we do. However, identifying, understanding and effectively managing the risks that make the difference between creating opportunity and value and jeopardizing success is possible with the proactive approach of an organization with risk intelligence.
GRC – Governance, Risk management and Compliance (Governance, Risk (management) and C ompliance). For most organizations these concepts are familiar and have often been applied separately.
These disciplines, which constitute the triple pillars of the corporate and effective management approach, have been combined under an integrated model to form the GRC. and compliance processes are operating at an optimum level, to have an integrated risk management structure with all processes and to eliminate all uncertainties.
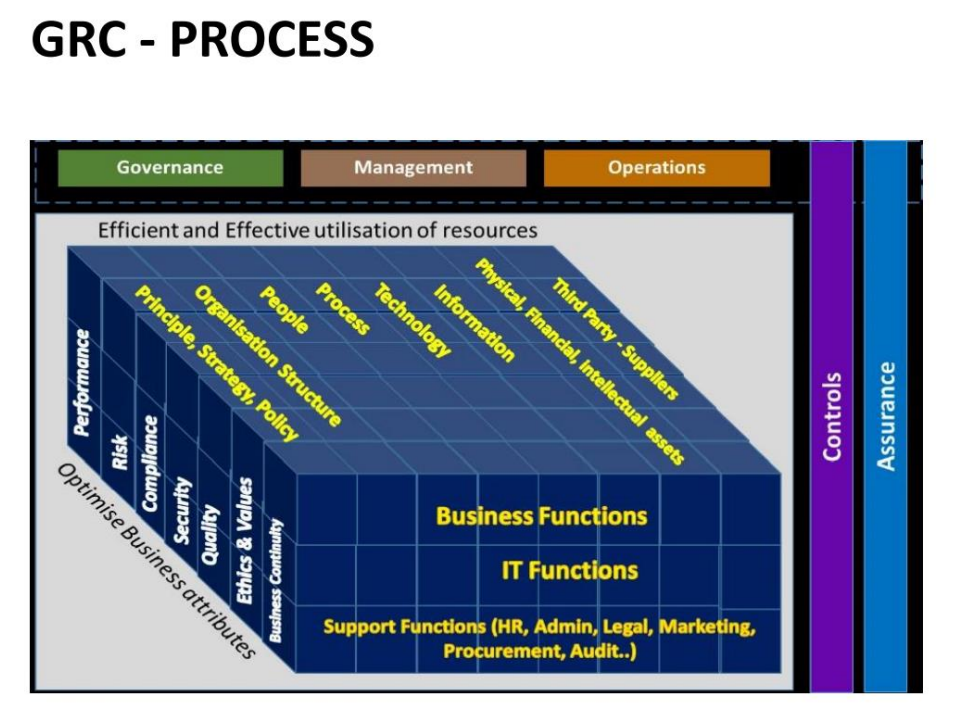
Governance
Governance is the set of policies, rules and frameworks a company uses to achieve its business objectives. It defines the responsibilities of key stakeholders such as the board of directors or senior executives.
The basic requirements for good governance can be listed as “ethical management principles, transparent information sharing, conflict resolution policies and effective resource management”.
Risk Management
Organizations face different types of risks, including operational, financial, legal, strategic and security risks. Proper risk management helps companies identify these risks and find ways to correct them when they occur.
The enterprise risk management program is used to anticipate potential problems and minimize losses. For example, you can use risk analysis/assessment to find vulnerabilities in your computer system and apply necessary fixes.
Suitability
Suitability; is the act of following rules, laws and regulations. Legal and regulatory requirements set by industry authorities also apply to internal policies. Compliance at the GRC includes applying procedures to ensure that company operations comply with applicable regulations.
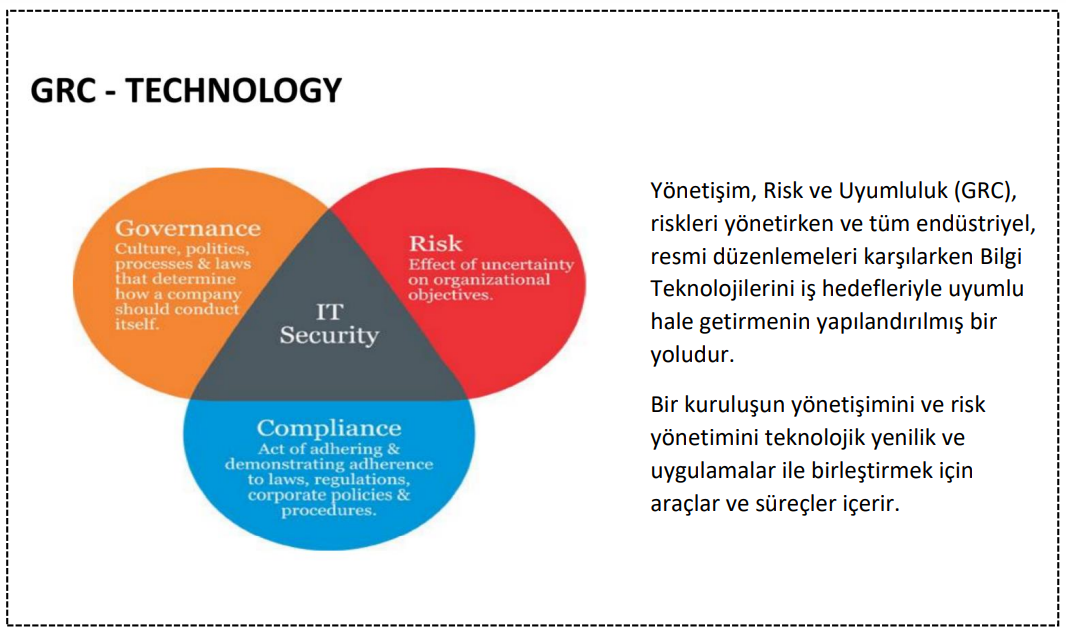
Why is GRC Important?
Institutions can take more effective decisions with a risk-sensitive management approach in line with GRC programs. An effective GRC program helps key stakeholders set policies from a shared perspective. The entire institution with the GRC; meet at a common point when it comes to policies, decisions and actions.
Some advantages of applying the GRC program can be listed as follows:
Making Data-Based Decisions
By monitoring your resources, setting rules or frameworks, as well as using GRC software and tools, you can make data-driven decisions in a shorter timeframe.
Responsible Operations
GRC facilitates operations around a shared culture that promotes ethics and creates a healthy environment for growth. It guides the development of a strong corporate culture and making ethical decisions in the organization.
Advanced Cyber Security
Companies can take data security measures to protect customer data and proprietary information with an integrated GRC approach. Implementing a GRC strategy is critical, given the increasing cyber risks that threaten users' data and privacy. It helps organizations comply with data privacy regulations such as GDPR, KVKK and information security standards such as ISO/IEC 27001, ISO/IEC 27701.
GRC Framework
The GRC framework is a model for managing governance and compliance risk in the organization. It involves identifying key policies that guide the organization in achieving its goals. By adopting the GRC framework, you can take a proactive approach to reducing risks, making informed decisions, and ensuring business continuity.
You can start implementing GRC by adopting GRC frameworks with key policies aligned with your strategic goals. Key stakeholders base their work on a shared understanding of the GRC framework when formulating policies, structuring workflows, and managing the company. Software and tools can be used to coordinate and monitor the success of the GRC framework.
GRC Maturity
GRC maturity is the level of integration of governance, risk management and compliance in an organization. You reach a high level of GRC maturity when a well-planned GRC strategy results in cost efficiency, productivity, and risk mitigation effectiveness. A low level of GRC maturity is inefficient and causes business units to continue operating in *silos.
* “Silo” is a term generally used to express disjointed departments in large companies.
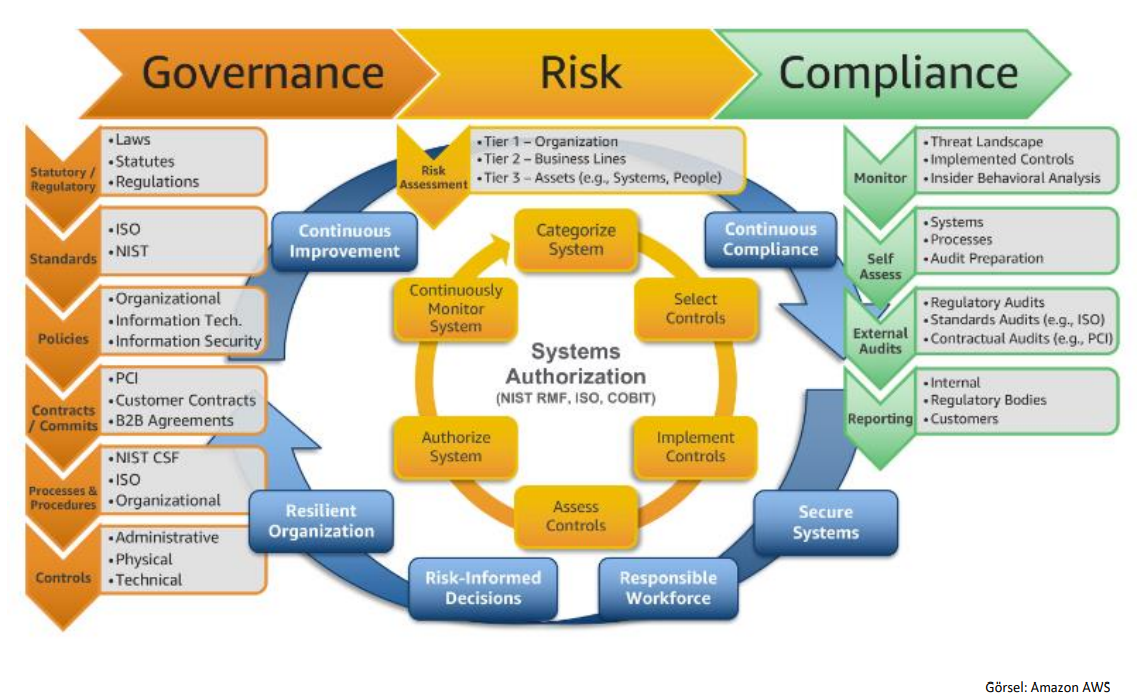
Sustainable GRC Model
The Sustainable GRC Model contains guidelines that help companies achieve performance based on GRC implementation and established principles. Communication provides a shared understanding of policies and education. You can take a holistic, structured and sustainable approach to integrating your GRC operations into your organization.
It is critical that your strategy, actions, and goals are aligned, and you can do this by considering opportunities, threats, values, and decision-making requirements.
GRC encourages you to take actionable action, avoid blocking targets, and monitor your operations to detect momentary changes.
Re-examine your strategy and actions to make sure they align with your business goals.
Economic sustainability is based on the establishment of strategies developed to ensure the benefit relationship between the enterprise and the society by using the available resources in an optimal way. While this concept covers the asset allocation processes for institutions to maximize value, it adopts the principle of managing organizational resources in the most optimal and sustainable way.
The main role in the sustainable GRC is in the Governance component.
Governance defines and carries out the management of the sustainability of all components that make up the structure, especially the competence of the employees, company policies and procedures, organizational structure and technology.
Sustainability refers to the consumption of resources to meet current needs without compromising the ability of future generations to meet their own needs. The aim of the sustainability strategy is to create value in the form of efficient and ethical use of natural resources and social capital.
The main drivers of sustainability in organizations are business risks and compliance with environmental and legal regulations. Sustainability and GRC are inextricably linked.
The COVID-19 pandemic has highlighted how unpredictable the economy and the free market really are. In an environment of increasing uncertainty, changing attitudes and inconsistent regulations, businesses face numerous risks. Legal risks, operational risks, changing customer demands and expectations and the resulting reputational risks need to be managed. According to the World Economic Forum's 2019 global risks list, increased investor interest in climate change is driving broader consideration of the financial implications of systemic environmental and social risks. A solid corporate sustainability strategy is an effective tool for mitigating and managing such risks.
A corporate sustainability strategy can provide more insight from a holistic perspective, even when viewed in the context of GRC functions, even when it is not explicitly designed as a risk mitigation tool. It can create a list of strategic actions that reduce duplication and redundancy and optimize resource usage. Used together, these strategies can help an organization achieve business goals, address uncertainty and act with integrity through good business practices. Eliminating internal silos and promoting data sharing within the organization is integral to identifying and utilizing such strategic synergies.
Sustainability has definite potential to be used as an effective risk management strategy. However, the effectiveness of this strategy depends on the individual organization and how it implements the strategy. Gaining in-depth knowledge of the company's operations, identifying all types of risks, and creating a sustainability strategy to manage those risks is the biggest challenge facing businesses today.
New technologies such as Artificial Intelligence (AI), Design Thinking, and Advanced Data Analytics can be useful tools for prioritizing business goals.
AI-based software platforms can offer organizations an autonomous way to monitor the success of a sustainability strategy and measure its impact on the organization's governance, risk management and compliance framework.
A collaborative perspective that aligns sustainability functions with the GRC can provide stronger, more sustainable strategies to make businesses resilient to the changes and uncertainties of the future.
[vc_row][vc_column][vc_cta h2=”” add_button=”bottom” btn_title=”Teklif Talep Edin” btn_style=”flat” btn_shape=”square” btn_color=”danger” css_animation=”fadeInLeft” btn_link=”url:https%3A%2F%2Fcyberartspro.com%2Fteklif-isteme-formu%2F||target:%20_blank|”]Siber Güvenlik, Dijital Dönüşüm, MSSP, Sızma Testi, KVKK, GDPR, ISO 27001, ISO 27701 ve DDO Bilgi ve İletişim Güvenliği Rehberi başlıklarıyla ilgili teklif almak için lütfen tıklayın.[/vc_cta][/vc_column][/vc_row]












