Recent research has revealed a vulnerability in hand-over, a fundamental mechanism underpinning modern cellular networks that can be used by attackers to launch denial-of-service (DoS) and man-in-the-middle (MitM) attacks using low-cost equipment.
The problem affects all generations since 2G (GSM) and has not been resolved so far.
Relay, also known as Hand-Over, is a process in telecommunications where a phone call or a data session is transferred from one cell broadcast (aka base station) to another cell tower without losing connection during transmission. This method is essential for establishing cellular communication, especially in scenarios where the user is on the move.
The routine works like this:
The user equipment (UE) sends signal strength measurements to the network to determine whether a handover is required and, if so, facilitates the handover when a more suitable destination station is discovered.
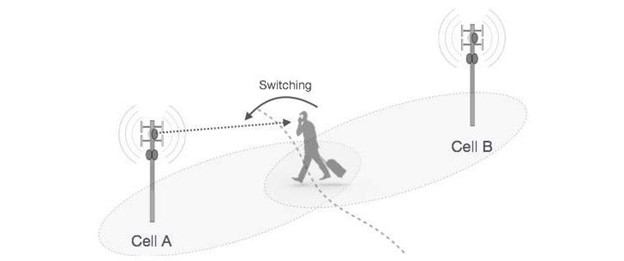
In fact, exactly in this part, we can find the answer to the question of how the security test can be done.
While these signal readings are protected as cryptographic, the content of these reports is not verified by the network, allowing an attacker to connect the device to a cell broadcast that is controlled by the attacker. The crux of the attack lies in the source base station’s inability to handle incorrect values in the measurement report, increasing the likelihood of a malicious hand-over without being detected.
In summary, we can perform one of our security tests by creating a fake base station.
It effectively enables the pentester to attack MitM, making hand-over procedures based on the above-mentioned encrypted measurement reports and signal strength thresholds vulnerable.
Therefore, thanks to this attack, it can listen to the messages transmitted between the device and the network, change their content and forward them to the victim user.
Installation of Hardware and Tools
Equipment::
Any of the following equipment can be used for practical purposes.
- RTL-SDR
- Hackrf
- USRP
Software:
The following software tools are required for practical purposes.
- GR-GSM – a python module used to receive information transmitted by GSM.
- Wireshark – Capture wireless traffic.
- IMSI-Catcher – This program displays the IMSI number, country, brand and operator of mobile phones.
- GQRX – Software defined radio receiver.
- RTL-SDR Tools – Retrieve RTL SDR dongle information.
- Calibrate – Determine the signal strength.
Now that we understand our attack surface, in order to carry out this attack, we will first need to use IMSI Catcher, which will enable us to create a fake base station to find and monitor the phones within the area it covers, depending on the gravitational power.
The IMSI catcher working logic is as follows.
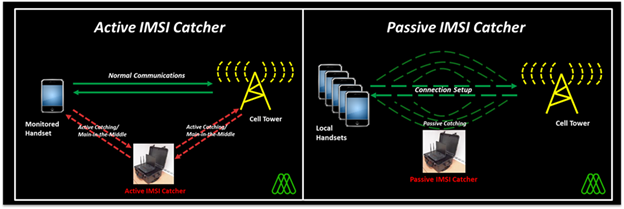
This device, for example; You can hackRF or use SDR Dongle.


Security Test Steps
a) Capture GSM Traffic
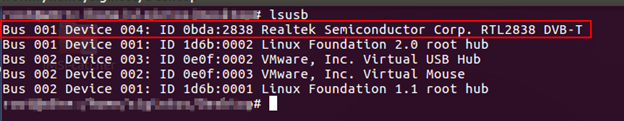
RTL-SDR dongle was used for this step. After the tool installation is complete, plug the RTL-SDR USB dongle into your system.
Open terminal and run the command below to check that the dongle is successfully mounted.
b) Calling GSM Base Stations
You can discover nearby cell towers using the “Calibrate” or “grgsm_scanner” tools.
![]()
In the output of the search we made with the tool above, the center frequency, channel, ARFCN value, LAC, MCC, MNC value, etc. of the base stations near us. We were able to obtain some parameter information such as.
c) Sniffing Base Station
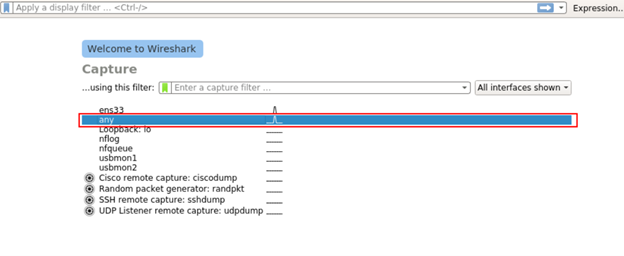
For this, it is necessary to use the program called “grgsm_livemon”. Run “Wireshark” before running the “grgsm_livemon” tool to capture packets. Select ‘any’ interface to capture all data.
When the frequency starts to be sniffed, a popup will appear as shown in the screenshot below.
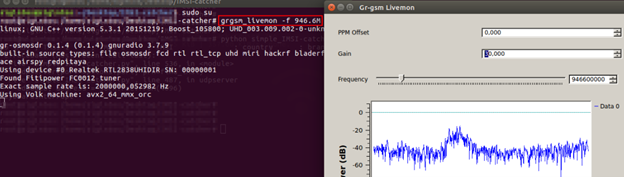
To catch the frequency, the frequency knob needs to be moved. When data capture starts, it will look like the screenshot below.
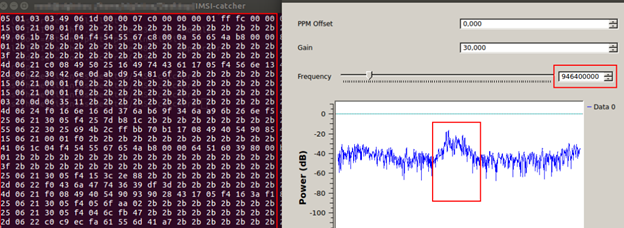
Now we need to capture the IMSI details with the help of an “IMSI Catcher” tool.
![]()
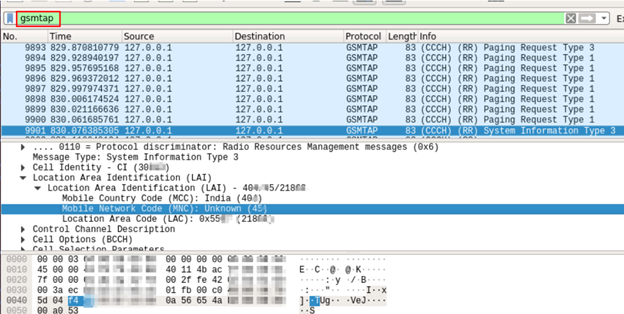
IMSI and TMSI, Country, Brand, Operator, MCC, MNC, LAC, Cell-ID etc. Run the “IMSI Catcher” tool to capture other details such as.

Captured data of base station’s MNC, MCC, LAI and other information can be seen in Wireshark.
How to Avoid and Detect IMSI Catcher?
There are different apps available to help you find IMSI Catcher where you are. When you install it on your mobile, it will automatically detect IMSI Catcher. The applications contain a database of base stations of all mobile operators in different countries and regularly updates this list.
When each base station is detected, it checks the list to see if it exists. If it does, it’s legitimate and not dangerous. However, if the tower is not listed, something suspicious is going on and there is a good chance it is an IMSI Catcher.
The best thing you can do in this situation is to turn your phone off and then back on when you reach a safe place.
Below are some of the IMSI Catcher Detector Applications::
- Osmocom
- Android IMSI-Catcher Detector
- SnoopSnitch
- Cell Spy Catcher
- GSM Spy Finder
Conclusion:
Cyber security architectures and cyber security layers should be built with more than one cyber security engineer. At the same time, we think that the tests should be done by cyber security companies that can bring different perspectives with more than one pentester, provided that the scope of the tests is wide.
Disclaimer
Dear visitor,
This blog post is for information purposes and has been prepared with the aim of raising awareness against attacks and taking measures in this direction. We remind you that it is not legal to use the information in this article for any other purpose. We declare that CyberArts company cannot be held responsible for direct or indirect damages and losses that may arise from what is explained.
[vc_row][vc_column][vc_cta h2=”” add_button=”bottom” btn_title=”Teklif Talep Edin” btn_style=”flat” btn_shape=”square” btn_color=”danger” css_animation=”fadeInLeft” btn_link=”url:https%3A%2F%2Fcyberartspro.com%2Fteklif-isteme-formu%2F||target:%20_blank|”]Siber Güvenlik, Dijital Dönüşüm, MSSP, Sızma Testi, KVKK, GDPR, ISO 27001, ISO 27701 ve DDO Bilgi ve İletişim Güvenliği Rehberi başlıklarıyla ilgili teklif almak için lütfen tıklayın.
[/vc_cta][/vc_column][/vc_row]












