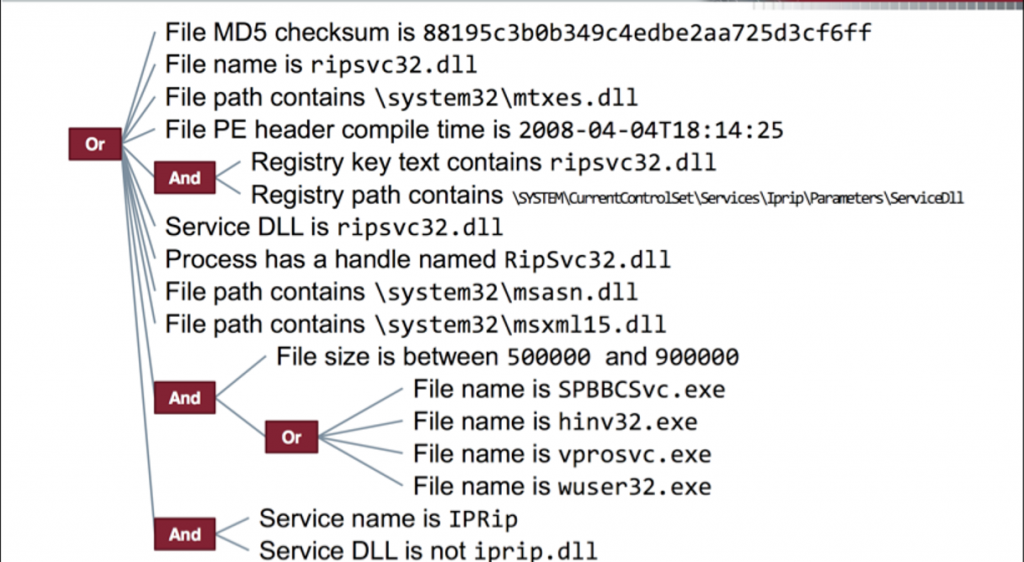
In simple terms, IoC can be expressed as evidence of a security breach, indicating inconsistencies or unusual activity in the organization’s network, that helps identify security threats, data breaches, insider threats, and more before harm can come from any cyberattack.
During a cybersecurity incident, indicators of compromise (IoC) are clues and evidence of a data breach. This evidence can reveal not only that an attack took place, but also what tools were used in the attack and who was behind these attacks.
IoCs not only act as a warning sign for impending attacks, but also help analyze what is happening. IoC data is collected after a suspicious event or packet flow over the network.
IoCs can also be used to determine the extent to which a compromise affects an organization and collect lessons learned to help protect the attack surface from future attacks. Indicators are often collected from software, including anti-malware and antivirus systems, but other artificial IoC cybersecurity tools can be used to collect and organize indicators during incident response.
IoCs are helped by experts to detect malicious activity. It is possible to detect malicious activities in the network early and intervene in a short time.
Tracking IoCs allows the organization to better perform at detecting and responding to security events. With the data it provides, IoCs help experts make informed decisions faster and more accurately.
Data that can be IoC;
- Abnormal actions of privileged users
- Deviant DNS requests
- Excessive increase in web traffic
- Increased database reading
- Growing HTML response sizes
- More than normal requests on the same file changes to the registry.
- Unusual changes to the registry
- Unknown files, apps and processes on the system.
- Network traffic showing Brute Force attacks
- IP addresses from different geographies
IOC Formats
- MISP Malware Information Sharing Platform & Threat Sharing format – Features used in the MISP project, including the MISP kernel format.
- Miter cyber observable eXpression (CybOX ™)- This site contains archived CybOX documentation.
- Miter malware attribute Enumeration and Characterization (MAEC™) – A scheme for understanding malware.
- Miter structured Threat Information eXpression (STIX™) – A structured language for cyber threat intelligence.
- Wound – Pattern matching for malware researchers (and everyone else).
- Swiss knife. mandiant /OpenIOC_1.1- This repository contains a revised schema, iocterms file, and other supporting documents that form the basis of the outline of the revised OpenIOC version we call OpenIOC 1.1.
Source of Compromise Indicator (IoC):
Reconciliation indicators can come from many sources and they fall into two categories of external agencies or internal sources.
External Agencies:
Outside agencies can be commercial or industry sources, or free IoC resources you can get online like the IOC bucket and MISP.
For example. Examples of commercial IoC resources are your antivirus or anti-malware vendors, and they all have a large library or collection of IoCs used. Some of the important free IoC resources we can use are Malware Information Sharing Platform or MISP and AlienVault OTX is a great resource in many different areas and there is also a dedicated IOC Buckets that lets you create your own IoCs and share them across the community.
Internal Resources:
There are several different ways we can collect logs and events that allow us to analyze and actually detect IoCs. These can come from commercially available systems, some free-to-use systems. (Like internal logs and event viewers). Some of the important ones will include unusual outgoing network traffic and geographic anomalies. An example of this would be your account users logging in from foreign locations or performing some kind of risky login activity, once again you can also detect IoC single sign-on failures by looking at a potential attack against one of your user accounts, increase in database read volume or You can also detect anomalies in traffic such as HTML response size anomalies, unusual DNS requests, and suspicious file and registry changes.
Why Use the IOC?
IOCs provide more context for security operations centers to know what is going on in the global threat landscape and the ability to scan their internal networks for such networks. This allows you to get up to speed so you can do history browsing and prioritize resources, so you know what to focus on.
Indicators of Consensus (IoC) Work?
Although malware authors always try to create software that avoids detection, every application leaves evidence of its presence on the network. These clues can be used to determine if the network is under attack or if a data breach has occurred. Forensic investigators use these clues to prepare countermeasures after a cybersecurity incident and gather evidence to file criminal charges against an attacker.
Think of compromise indicators as traces left by an attacker after a cybersecurity incident. Anti-malware applications can partially stop the event, but security breach indicators determine data and files that an attacker can access. They are especially important in finding vulnerabilities and exploits used by attackers to steal data because they inform the organization about ways to better protect the network in the future.
Types of Compromise Indicators:
IoCs fall into two main categories:
Network Based Indicators
Network-based indicators. These refer to everything related to the network connection. The URL of a website is a malicious indicator. A domain name can also be thought of as a Compromise Indicator. An infection scenario might involve redirecting all requests for a particular domain to a malicious website. IP addresses can be used as alternatives to URLs. For example, they can be embedded in malicious scripts to be used to download second-stage malware.
Examples:
- URL
- Web Site
- Domain
- IP address
Host Based Indicators
The second important category is host-based indicators, these artifacts that can be found in a computer system itself. Windows-type malware uses certain locations to execute automatically even after the computer restarts. A special type of indicator is file hashes. These help us uniquely identify files based on their content. Examples:
- File name
- Path
- File Fingerprint or Hash
- File extention
- File location
What Are Examples of Compromise Indicators?
There are several indicators of compromise that your IT and information security teams should consider. Below you can find the 15 most obvious indicators of reconciliation.
- Anomalies Found in Privileged User Activity
- Red flags found on login event
- Perverted DNS requests
- Web traffic with inhuman behavior
- Unusual activity in outgoing network traffic
- Geographic abnormalities
- Increased database read volume
- Unusual HTML response sizes
- Changes to mobile device profiles
- DDoS activity
- Misplaced data packets
- Conflicting port-application traffic
- More requests than usual for the same file
- Unusual changes to registry and/or system files
- Sudden patching of systems
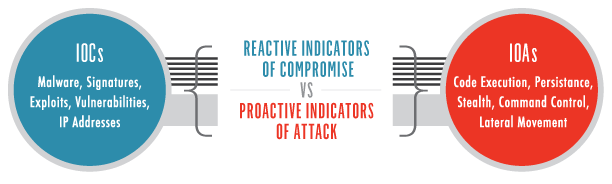
Compromise indicators (IoC) and attack indicators (IoA)
What is IoC compared to IoA? Cybersecurity incidents have several stages. But in terms of investigations, there are two main concerns: Is the attack ongoing, or has the matter been brought under control? Researchers use indicators of compromise left by an attacker to answer both questions.
IoC security used during the incident response is used to determine the scope of an attack and data breached. Attack indicators (IoA) are used to determine whether an attack is underway and should contain it before it can cause more damage.
Both IoC cyber tools and IoA tools work with evidence and metadata that give researchers clues about the status of an attack. Compromise indicators are used when, after an attack is under control, the organization needs to know where, what, and how. Attack indicators focus on an existing attack that may be active and needs to be contained.
For highly secretive malware, a compromise can take months before administrators realize it. IoAs will help determine whether the suspicions are true or false positives.
Indicators of Compromise (IoC) and Indicators of Attack (IoA)?
Compromise indicators serve to detect security events and compromises, while attack indicators serve to detect attacker intent. To successfully contain and stop the attack, it is important to know what the attacker is trying to achieve. This is why attack indicators are important.
Compromise indicators help IT professionals and cybersecurity teams detect any intrusion, but to stop this intrusion, your security teams need to know what the attacker is planning. Knowing the attacker’s next move and intent gives the security team an edge.
Therefore, the data collected by the compromise indicators should be supported by the attack indicators.
Examples and types of consensus indicators
Large networks can have thousands of IOCs. Therefore, most evidence is collected and uploaded to IoC, SIEM systems to help forensic investigators organize the data. Evidence can come from a multitude of places, but here are a few items of discovery that can be used as an IoC:
- Unusual outbound traffic: Attackers use malware to collect and send data to an attacker-controlled server. Outbound traffic during off-peak hours or traffic communicating with a questionable IP can indicate an IoC security threat.
- High-privilege user activity irregularities on sensitive data: Compromised user accounts are used to access sensitive data. A high-privilege user account is required for an attacker to access data that has been locked from standard user accounts with basic permissions. A high-privilege user account accessing sensitive data during off-peak hours or infrequently accessed files could indicate that their credentials were phishing or stolen.
- Activity from strange geographic regions: Most organizations have traffic from a targeted region. State-sponsored attacks and those from countries outside of the organization’s targeted geographic area generate traffic indications outside of normal zones.
- High authentication errors: In account hijacking,attackers use automation to authenticate using phishing credentials. A high rate of authentication attempts may indicate that an attacker has stolen credentials and is trying to find an account that gains access to the network.
- In database reads: Whether it is adding SQL or accessing the database directly using an administrator account, dumping data in database tables can indicate that an attacker has stolen data.
- Excessive requests to important files: Without a high privilege account, an attacker would have to investigate different exploit attempts and find the right vulnerability to access files. Multiple access attempts from the same IP or geographic region should be reviewed.
- Suspicious configuration changes: Changing configurations on files, servers, and devices can provide an attacker with a second backdoor on the network. Changes can also add vulnerabilities that malware can exploit.
- Traffic overflowing to a specific site or location: A compromise on devices can turn them into a botnet. An attacker sends a signal to the compromised device to overflow traffic to a specific destination. High traffic activity from multiple devices to a given IP can mean that internal devices are part of a distributed denial of service (DDoS). dağıtılmış hizmet reddinin (DDoS) bir parçası olduğu anlamına gelebilir.
A consensus indicator can be defined as one or more of these indicators. A forensic investigator’s job is to examine all IoC evidence to determine which vulnerability has been exploited.
IoC Security Detection to Improve Response
After an incident, IoC cybersecurity measures can be used to identify what went wrong so the organization can avoid future exploits of the same vulnerability.
In some cases, organizations cannot properly log and monitor the right resources. This surveillance leaves them open to an attacker who can avoid detection after an investigation. It is important to first implement network monitoring to detect an attack, but logs and audit trails are equally important for investigations.
IoC data points can be collected in real time during an investigation to reduce response time. SIEMs are used to separate noise from the valuable evidence needed to identify an attack and its attack vectors. Documenting existing incident response procedures can also reduce the time required for an investigation. These procedures should be reviewed after a compromise to improve them.
During incident response, the “lessons learned” phase is the final step. The IOCs will be helpful at this stage to determine which cybersecurity defenses are misconfigured or insufficient to stop an attacker. The more extensive logs and audit trails an organization has, the more effective its investigations will be during incident response.
To request a quotation for the following: Cyber Security, Digital Transformation, MSSP, Penetration Testing, KVKK, GDPR, ISO 27001 and ISO 27701, please click here.