Otomobil sızma teknikleri, farkını ortaya koyan alanlardan biri gibi dursa da günümüz ve gelecek için önem taşıyan test yöntemlerinden biri olacaktır. Otomobillerimiz giderek daha akıllı hale geldikçe, giderek daha fazla elektronikleştikçe otomobilleri daha savunmasız hale getiriyor.
Kelimenin tam anlamıyla sürücüsüz veya otonom araba çağına dönüştüğümüz için, otomobillerin güvenlikleri önemli hale geldi ve gelmeye devam edecek.
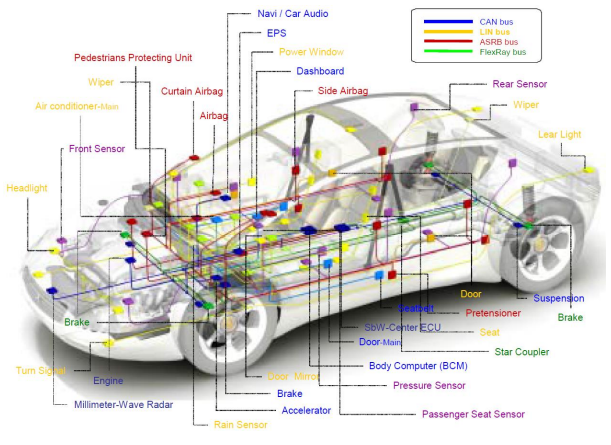
Otomobil sızma tekniklerine geçmeden önce, temelleri anlamamız gerekiyor. Otomobil elektroniği, çoklu mikro kontrolörler, sensörler, göstergeler, aktüatörler vb. arasında iletişim kurmak için birkaç farklı protokol kullanır. Bu protokollerin en yaygın olarak kullanılanı Controller Area Network veya CAN’dır.
CAN, Ağdaki her düğüm, her iletimi “görebilir”. Ethernet veya TCP/IP’den farklı olarak (ancak SCADA sistemlerindeki modbus’a benzer şekilde) tek bir düğüme mesaj gönderemezsiniz, ancak CAN yerel filtreleme sağlar, böylece her düğüm yalnızca kendi çalışmasıyla ilgili mesajlara göre hareket eder. Bunu, içeriğin hedef düğümü belirlediği “içerik mesajlaşması” olarak düşünebilirsiniz.
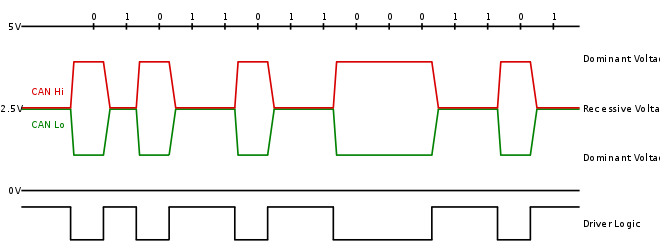
CAN; yüksek ve düşük olmak üzere iki kablo üzerinden çalışır. Otomobil sistemlerinin doğasında bulunan “gürültü” nedeniyle CAN, diferansiyel sinyalleme kullanır. Bu, protokolün iletişim kurmak için iki kablodaki voltajı yükselttiği ve azalttığı yerdir. Hem yüksek hızda hem de düşük hızda CAN’de sinyalleme, sıfır (0) iletirken yüksek kabloyu 5v’ye ve düşük kabloyu 0v’ye doğru sürer. Ancak bir (1) gönderirken her iki kabloyu da sürmez.
CAN dört (4) farklı türde mesaj kullanır;
- Data Frame
- Remote Frame
- Error Frame
- Overload Frame
Data Frame
Bu aslında veri iletimi için kullanılan tek çerçevedir. Çoğu durumda, veri kaynağı nodu veri çerçevesini gönderir. Standart ve genişletilmiş olmak üzere iki çeşidi vardır. Standardın 11 tanımlayıcı biti ve genişletilmişin 29 biti vardır. CAN standardı, temel veri çerçevesinin MUTLAKA kabul edilmesini ve genişletilmiş çerçevenin MUTLAKA TOLERANS EDİLMESİNİ gerektirir. Başka bir deyişle, protokolü veya iletimi bozmaz.
Remote Frame
Veri hedef düğümü kaynaktan veri istediğinde kullanılır.
Error Frame
İki farklı alanı vardır, ilki Error Flags tarafından verilir ve farklı istasyonlar tarafından katkıda bulunur. Ve ikincisi, sadece hata mesajının sonunu gösteren Error Delimeter’dir.
Overload Frame
Overload Frame’in iki alanı vardır. Bunlar Aşırı Yük Bayrağı ve Aşırı Yük Sınırlayıcıdır. Aşırı yük çerçevesi, bir alıcının dahili koşulları veya iletim sırasında baskın bit (0)’ın algılanmasıyla tetiklenir.
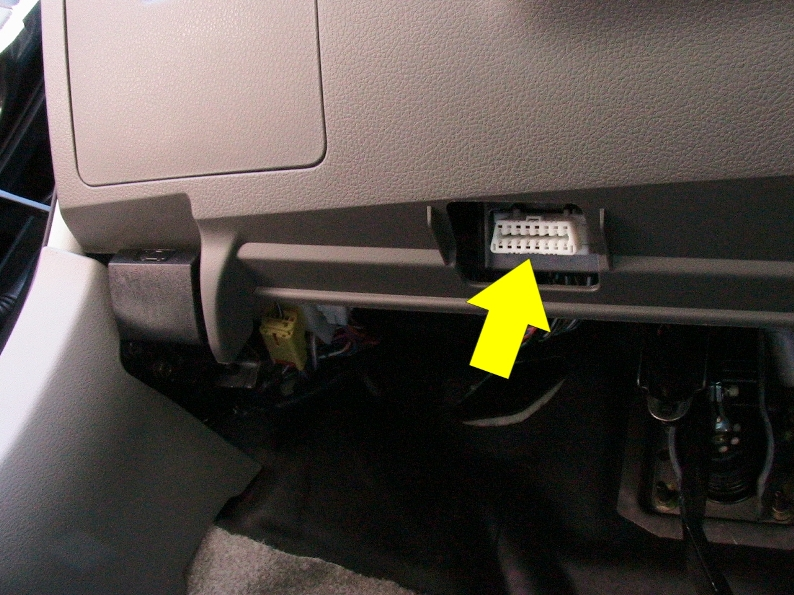
Yerleşik Tanılama (OBD)-II Konnektörü
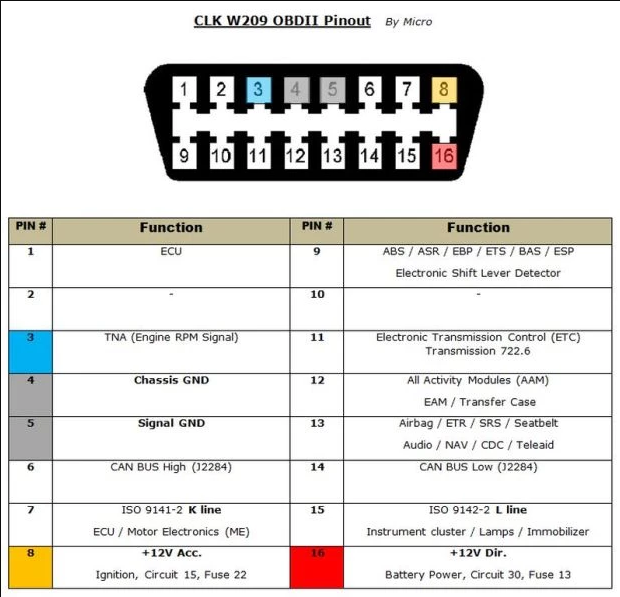
Çoğu araç bir ODB-II konektörü ile birlikte gelir. Arabanızı tamir için bir dükkâna götürdüyseniz, tamircinin bilgisayar ile bir okuma almak için bilgisayarını bağladığı, gösterge panelinin altındaki bu konektördür.
OBD-II’nin 16 pimi vardır ve aşağıdaki şemaya benzer.
Bir pentester olarak biz de bu OBD-II konnektörüne bağlanıp CAN ağı üzerinden çeşitli cihazlara mesaj gönderebiliriz.
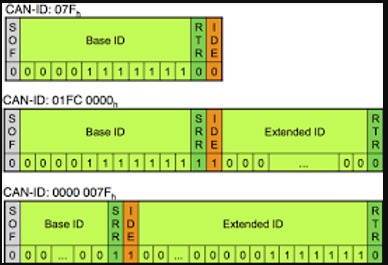
CAN Bus Paket Düzeni
Standart ve genişletilmiş olmak üzere iki tür CAN paketi vardır. Genişletilmiş paketler, standart paketle aynı öğeleri paylaşır. Ancak genişletilmiş paketler, kimlikleri dahil etmek için ek alana sahiptir.
Standart Paketler
Her CAN paketinin dört kritik bölümü vardır. Bunlar;
- Arbirition ID
Paketi gönderen cihazın kimliğidir.
- Identifier Extension
Bu bit, standart CAN için her zaman 0’dır.
- Data Length Code (DLC)
Bu, 0 ila 8 bayt arasındaki verilerin boyutunu gösterir.
- Data
Bu, mesajdaki verilerdir. Yukarıda belirtildiği gibi, 8 byte kadar olabilir.
Yukarıda bahsedildiği gibi, tüm CAN paketleri yayınlanır. Böylece her cihaz veya kontrolör her paketi görebilir. Herhangi bir aygıtın paketi hangi denetleyicinin gönderdiğini (dönüş adresi yok) bilmesinin bir yolu yoktur. Bu nedenle CAN ağındaki sahte mesajlar önemsizdir. Bu, CAN’ın temel zayıf yönlerinden biridir.
Genişletilmiş CAN Paketleri
Genişletilmiş CAN paketleri, standart CAN paketleriyle aynıdır. Ancak daha uzun kimlikler oluşturmak için birlikte zincirlenirler. Genişletilmiş CAN, standart CAN ile geriye dönük olarak uyumludur. Bu, bir sensor genişletilmiş CAN paketlerini kabul edecek şekilde tasarlanmadıysa, bu sistemin bozulmayacağı anlamına gelir.
Güvenlik
CAN düşük seviyeli bir protokol olduğundan, yerleşik herhangi bir güvenlik özelliğine sahip değildir. Varsayılan olarak şifreleme veya kimlik doğrulaması YOKTUR. Bu, ortadaki adam saldırılarına (şifreleme yok) ve sızdırma saldırılarına (kimlik doğrulama yok) yol açabilir. Bazı durumlarda üreticiler, yazılımın değiştirilmesi ve frenlerin kontrol edilmesi gibi kritik görev sistemlerinde kimlik doğrulama mekanizmaları uygulamışlardır, ancak bunlar tüm üreticiler tarafından uygulanmamıştır. Parolaların uygulandığı durumlarda bile, kırılmaları nispeten kolaydır.
Bu içerik dizisinin diğer bölümlerine aşağıdaki linklerden ulaşabilirsiniz:
- Yeni Nesil Otomobil Güvenlik Testleri Nasıl Yapılmalı? [2]
- Yeni Nesil Otomobil Güvenlik Testleri Nasıl Yapılmalı? [3]
- Yeni Nesil Otomobil Güvenlik Testleri Nasıl Yapılmalı? [4]
Sorumluluk Reddi Beyanı
Değerli ziyaretçimiz,
Bu blog yazımız bilgi amaçlı olup, saldırılara karşı farkındalığı arttırabilmek ve bu doğrultuda tedbirler alınabilmesi amacı ile hazırlanmıştır. Bu yazıda geçen bilgilerin amacı dışında kullanılmasının hukuki olmadığını hatırlatırız. Anlatılanlardan kaynaklanabilecek doğrudan ya da dolaylı zarar ve kayıplardan CyberArts firmasının sorumlu tutulamayacağını beyan ederiz.
Siber Güvenlik, Dijital Dönüşüm, MSSP, Sızma Testi, KVKK, GDPR, ISO 27001, ISO 27701 ve DDO Bilgi ve İletişim Güvenliği Rehberi başlıklarıyla ilgili teklif almak için lütfen tıklayın.